(Reading time: 9 minutes)
There’s never a good time to be homeless—but there’s bad, and then there’s infernally bad. We’re now well into Dante territory, hurtling past limbo, lust and gluttony to start ricocheting off greed’s boulders.
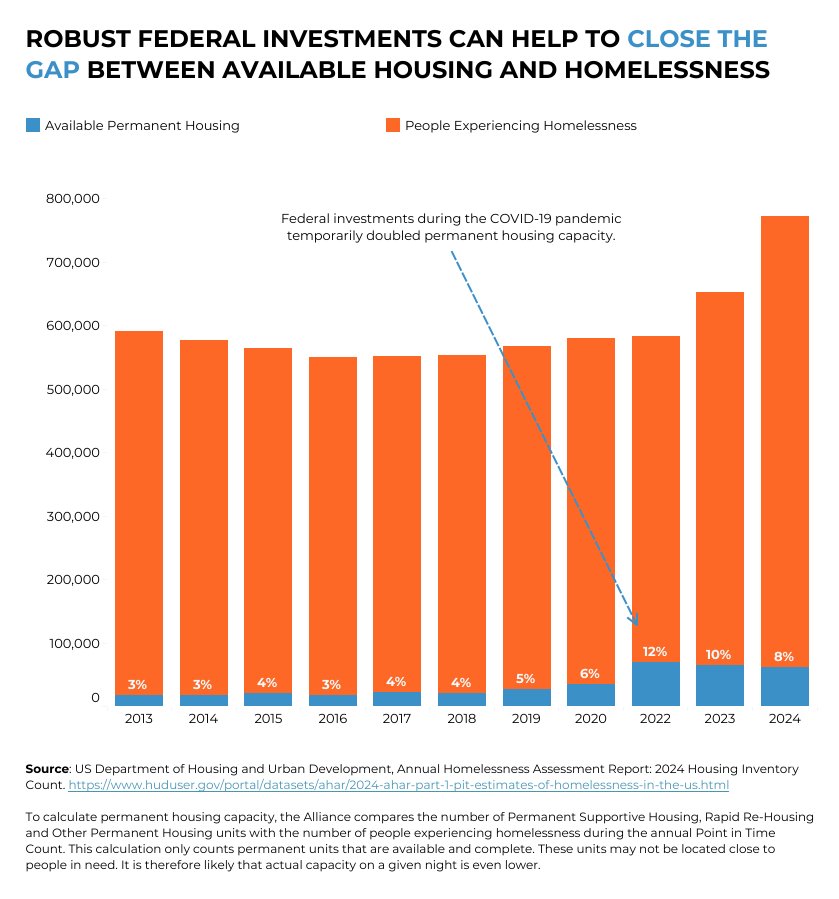
On a federal level, the gap between supply and demand for housing for the homeless was already skyrocketing before the Trump administration took office (graphed above) but exploded in the past year, thanks to a combination of funding rescissions and deep staffing cuts in departments serving the poor and unhoused. That notably includes the departments of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) and of Health and Human Services, which just in the past couple of days have been whacked with further unprecedented layoffs, shredding what little remains of an already tattered social safety net. If there’s any doubt about the local implications of all this, see the Blue Ridge Area Food Bank and its increasingly alarmed appeals for community support.
But there’s also a deeper, more profound shift in housing policy underway that will have the perverse effect of pouring gasoline on the fire. That shift dates back to a July executive order, issued by Donald Trump under the provocative title “Ending Crime and Disorder on America’s Streets,” that ends support for the “Housing First” approach to a growing unsheltered population. While Housing First advocates contend (often with references to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs) that people’s basic needs for food, warmth and shelter must be met before they can effectively address addictions, psychological ills or lack of job training, the executive order claims Housing First policies “deprioritize accountability” and fail to “promote treatment, recovery and self-sufficiency.” The better approach, according to the executive order, is to slash funding for such assistance while instituting sobriety requirements for people living in federally funded housing. Can’t stay straight? It’s back on the street with you, where the physical struggle for survival will take all your energy.
Meanwhile, the current trend toward criminalizing homelessness only adds to the problem. A U.S. Supreme Court decision last year empowered municipal officials to fine, ticket, displace or arrest people sleeping in public spaces, and more than 200 localities around the country have since criminalized homelessness. But other jurisdictions—including Staunton, Waynesboro and Augusta County—already had similar laws on their books. And while our local law enforcement agencies thus far have taken a restrained approach to people camping on public property, acting mostly in response to complaints by directing the offenders to move elsewhere, that could change with any pronounced shift in the political climate.
Homeless people who get jailed for failing to have a sanctioned place to sleep become, ironically, ineligible for certain housing programs. No surprise, then, that once they’ve been incarcerated for not having shelter, many end up in a cycle that perpetuates their homelessness. More than 50,000 people who are released from prison or jail each year go straight into homeless shelters and then into the streets, according to the National Alliance to End Homelessness, which reports that formerly incarcerated people are ten times more likely to become homeless than the general public due to a lack of financial and social support.
What little support for the homeless that still exists is being chopped away almost on a weekly basis. As reported by Politico a couple of weeks ago, the Trump administration is looking to move as much as two-thirds of HUD’s funds designated for permanent housing projects to transitional housing assistance “with some work or service requirements.” Those who can’t meet the requirements—such as a mother with young children, or someone who’s disabled—may end up on the street again, but as explained by a HUD spokesperson, “HUD is no longer in the business of permanently funding homelessness without measuring program success at promoting recovery and self-sufficiency.” That’s consistent with the administration’s overall “suck-it-up-buttercup” approach to social services but does nothing to address root causes, leaving it up to overwhelmed and unfunded local agencies to deal with the fallout.
Some of these issues may be addressed Monday evening at Kate Collins Middle School in Waynesboro, when Building Bridges for the Greater Good will host a forum on teenage homelessness. That’s because homeless teens are supposed to be served by the McKinney-Vento Homeless Assistance Act, which created the Continuum of Care (CoC) program that Politico reports is under attack—indeed, as Politico also noted, Trump’s budget for the next fiscal year proposes cutting all CoC funding. Loss of those funds will mean dozens of students in the SAW region who currently receive emergency housing, transportation and other necessities of life, including food, clothing and personal care supplies, will be at risk of losing their ability to stay in school.
CoC funding also assists 22 households in a program of permanent supportive housing administered by the Valley Community Services Board (VCSB), but their future is equally uncertain. The current funding runs out in December, and while a larger successor grant has been approved, there’s no certainty that money will be released. “If the Politico article is correct, this program would certainly be in jeopardy, but I am not sure what calendar year we will actually feel the impact,” said Lydia Campbell, assistant director of community services at VCSB. “It’s terrible that our community members with the most significant barriers to housing that are finally in their own places could be at risk.”
In the face of this onslaught, local efforts to cope with homelessness and a severe shortage of affordable housing have been lame, at best. That’s partly due to a lack of money, of course, but being cash-poor is insufficient excuse for a city that spends big bucks on a new pool house, golf carts and 50-gallon trash cans for everyone—all welcomed expenditures contributing to Staunton’s quality of life, but at the cost of letting internal sores fester. With only so many tax dollars to go around, expenditures in one area mean belt-tightening in another. In the end, it all comes down to the choices we’re willing to make—or ignore.
Take, for example, the request to city council by Alec Gunn, director of the Waynesboro Area Refuge Ministries (WARM), for financial support for a day center for the homeless at First Presbyterian Church. As initially conceived, this would have been a warm day-refuge in the winter and a cool one in summer for an unsheltered population that otherwise resorts to camping out in the library or in fast food restaurants to escape the weather. Talk of the city providing some modest start-up money for such an effort, perhaps $30,000, has been kicking around since the start of the year, with little to show for it and with ambitions for the day center’s scope of services diminishing with each passing month. More recently, rumblings of resistance from the church’s neighbors have been heard, and Gunn did himself no favors with the skimpy “budget” he presented to city council in early September—but neither has anyone on city council stepped up to press for a resolution. And so. . . still no day center.
As much—or little—can be said of the city’s pursuit of affordable housing, a critical component of any serious effort to eliminate homelessness. A key to this somnolent exercise has been creation of a housing commission that could “provide expertise and guidance regarding the amount and quality of affordable and workforce housing in the City,” an initiative first proposed by Councilor Brad Arrowood in March. That’s March of 2023. This past Thursday the city council finally received a resolution to do just that—but it won’t actually vote on the measure until an unspecified “later date.”
Not that there’s anything to be lost in this slow-walk to another grouping of chin strokers. Six of the proposed nine commission members are to be drawn from the ranks of the housing strategy working group that labored for a whole eight hours spread over 12 months to produce the city’s “housing strategy.” That group served mainly as a sounding board for city planners to present their ideas, and for the most part it resonated in tune; this was not a group brimming with ideas. The new commission will likewise meet only four times a year and, under the influence of its carry-over members, presumably will serve a similar role, with similarly minimal results. If there is to be any hope for the housing commission to provide meaningful input, it will have to come from the three non-working group members, ideally including representatives from the building and development sector and at least one person who has been homeless.
But first, of course, there actually has to be a city council vote to ratify the resolution. Assuming it does so in the next few weeks, and that the housing commission holds its first meeting in January, that will mark nearly three years since Arrowood’s initial proposal.
All this foot-dragging might be tolerable in a slower age, but that’s not where we are today. Instead, we’re hurtling toward a precipice with preternatural speed, the economy teetering toward recession, our political machinery seized up and normal middle-class people growing angry, suspicious and resentful under the weight of a disintegrating social order. How else to explain recent events in Waynesboro, where local residents circulated a letter deploring “the homeless problem” and criticizing St. John’s Episcopal Church for allowing a man to sleep in its bushes and a homeless couple to stay on an empty church lot. The letter expressed concern that mental illness, drug addiction and increased crime rates would put the neighborhood at risk, albeit without linking any of those problems to the three specific people prompting the writers’ angst.
Not all local residents shared that view, and in a couple of meetings pushed back vigorously against such stereotyping. But as the homelessness problem deepens and more people are forced to live in their cars and on the streets, similarly charitable responses may become more strained. We’re in a race against time that community leaders have not yet recognized, for money, effort, planning and initiative, and it would be reassuring to get even a whiff of urgency over what needs to be done.
